Keyboard Input
You can use the keyboard to operate DreamCalc either by using keystrokes or by putting
the calculator into the key focus mode.
Keystrokes
For many common tasks, using keystrokes is convenient and natural. For example, simply
type "5 + (3 * 72) =", and you will see the keys depress automatically and the input
appear in the numeric screen.
Keystroke input is not the same as "free text", however.
Functions, such as "sin", are accessed by single key press short-cuts rather than
by typing the name (to input the sine function, you would simply press "S" rather than typing out "s-i-n").
This method of input allows for speedier input once you are familiar with some basic keystrokes
(see below).
It is also possible to use a combination of keyboard and mouse, for example you can press the
keyboard SHIFT while clicking the calculator keys with the mouse.
Keystroke Hints
Right-click or hover your mouse over any key for function and keystroke information, as shown
below.
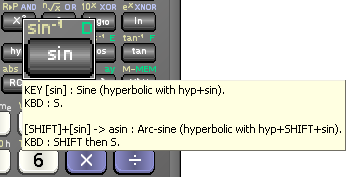
Right-Click on Keys for Help
Key hint and cursor behavior can be modified from the Options Windows.
Common Keystrokes
A full list of input keystrokes is presented below. However, some notable keystrokes are:
- Press "E" for [EEX].
- SPACE bar operates [+/(-)].
- The SHIFT key corresponds to [SHIFT] on the keypad.
- ESC or DELETE for [AC] (All Clear).
- Press "S", "C", "T" for Sin, Cos, Tan respectively.
- Press "R" for nth root function.
- ALT-S and ALT-R for [STO] & [RCL] respectively (see below).
- HOME key corresponds to [MODE].
- CTRL-I & CTRL-M to directly store and recall the MEM register.
- LEFT and RIGHT arrows operate the [ENG] key.
- You can use CTRL-C & CTRL-V for copy/paste as normal.
- Characters inputs "* / - + ^ % ! ( )" correspond to applicable operations.
- Keys on the numeric section of your keyboard control the corresponding keys on the calculator keypad
interface.
Key Focus Mode
Press TAB to toggle the key focus mode. In this mode, the key with input focus is
surrounded by dotted rectangle.
Key Input Focus
Press RETURN to activate the focused key.
Press "H" to show the key help hint (this is the same as right-clicking on the key).
DreamCalc's key focus behavior is similar to that of standard Windows input controls, however you should
use the arrow keys to move input focus rather than TAB. You can also use the
HOME and END keys to jump to the top and bottom of the keypad respectively, and PAGE UP
and PAGE DOWN to skip multiple rows. In key focus mode, keystrokes other than RETURN
and the arrow keys, work as normal.
Press TAB again to leave the key focus mode.
More About Keystrokes
Using SHIFT from the Keyboard
The keyboard SHIFT corresponds to the [SHIFT] key on the calculator.
To access a shifted function, you should generally press the SHIFT keyboard key but release it prior to pressing the
required function key. For example, to input the DOW function from the keyboard, type:
SHIFT (release and then) "8"
Inputs DOW (day of week - located on the [8] key).
Releasing the SHIFT key before pressing the next key helps DreamCalc to distinguish your keyboard input properly.
Often it won't matter, but in some cases keystrokes may otherwise conflict. For example, holding SHIFT while
pressing "8" on the keyboard would normally input the multiply (*) operation instead of DOW, as the "*" character
is normally located on the keyboard's "8" key and takes precedence.
Store & Recall Keys
Press ALT-S and ALT-R for the [STO] and [RCL] keys respectively, followed by the key naturally
representing the memory register you require. DreamCalc will know that the following key press should correspond
to a memory register, rather than a function.
For example:
ALT-S then "M"
Stores the current value to the MEM register.
or,
ALT-R then "E"
Recalls the value stored the E register.
Keystroke Reference
Scientific Keys
The following lists default input keystrokes for each function. If the calculator
is in base-N mode or the financial keypad is in use, other keystrokes may take precedence
however (see below).
- Toggle keypad roll-up
Keystroke: UP ARROW (or DOWN ARROW)
- Shift function key
Keystroke: SHIFT
- CONST
Access scientific constants on numerical keys
Keystroke: K
- ENG
SI engineering form (press repeatedly)
Keystroke: LEFT ARROW (or RIGHT ARROW)
- MODE
On-screen menus. Press again for next screen
Keystroke: HOME
- S-MODE
Change statistical mode
Keystroke: SHIFT then HOME
- COPY/PASTE
Copy or paste value from calculator
Keystroke: CTRL+C / CTRL+V
- Close DreamCalc
Keystroke: ALT+F4
- POLY
Polynomial solver
Keystroke: X
- Calculate nCr permutations
Keystroke: SHIFT then X
- S-SUM
Statistical SUM function menu
Keystroke: ALT+U
- <n> nPr <r>
Calculate nPr permutations
Keystroke: ALT+F8
- S-VAR
Statistical VAR function menu
Keystroke: ALT+V
- PG <z>
Gaussian integral over range [-INF, z]
Keystroke: ALT+F9
- S-DIST
Statistical DIST function menu
Keystroke: ALT+D
- QG <z>
Gaussian integral over range [0, z]
Keystroke: ALT+F10
- DAT
Add value to statistical data list
Keystroke: INSERT or ALT+ENTER
- RG <z>
Gaussian integral over range [z, +INF]
Keystroke: SHIFT then INSERT
- Separator for complex or list input values
Keystroke: "," (comma) or ";" (semicolon) or ":" (colon)
- zs <r>
Standard z-score for two-sided confidence level r
Keystroke: SHIFT then "," (comma) or ALT+Z
- <x>^-1
Inverse of x (1/x)
Keystroke: ALT+1 or ALT+NUM 1
- <x>!
Factorial of x
Keystroke: "!" (exclam)
- sqrt <x>
Square root of x
Keystroke: Q
- P→R <r + ti>
Polar to rectangular coordinate
Keystroke: SHIFT then Q or ALT+F11
- <x>²
Square of x
Keystroke: ALT+2 or ALT+NUM 2
- R→P <x + yi>
Rectangular to polar coordinate
Keystroke: ALT+F12
- <x> ^ <y>
Raise to any power
Keystroke: "^" (hat)
- <n> root <x>
Calculate nth root of x
Keystroke: R
- log <x>
Base 10 logarithm of x
Keystroke: O or ALT+L
- 10^<x>
Calculate 10 raised to power x
Keystroke: SHIFT then O
- ln <x>
Natural logarithm of x
Keystroke: L
- exp <x>
Calculate e raised to power x
Keystroke: SHIFT then L
- a b/c
Input or convert to natural fraction
Keystroke: Z
- d/c
Convert to improper fraction
Keystroke: SHIFT then Z
- DMS
Input or convert to degrees, minutes & seconds
Keystroke: ? or "'" (apostrophe)
- <x> logB <base>
Logarithm in any base
Keystroke: ALT+B
- hyp
Hyperbolic function (i.e. [hyp]+[sin])
Keystroke: H
- sin <x>
Sine (sinh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: S
- asin <x>
Arc-sine (asinh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: SHIFT then S
- cos <x>
Cosine (cosh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: C
- acos <x>
Arc-Cosine (acosh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: SHIFT then C
- tan <x>
Tangent (tanh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: T
- atan <x>
Arc-Tangent (atanh with [hyp] key)
Keystroke: SHIFT then T
- DATE
Input or convert to date value
Keystroke: D or #
- STO
Store a value to memory registers MEM, 0-9 or A-F
Keystroke: ALT+S
- arg <a + bi>
Argument (polar angle)
Keystroke: A
- RCL
Recall a value from memory registers MEM, 0-9 or A-F
Keystroke: ALT+R
- abs <a + bi>
Absolute value (magnitude)
Keystroke: ALT+A
- Open parenthesis (or RPN stack roll up)
Keystroke: PAGE UP or ( or [
- <a + bi> : conj
Conjugate of complex value (CPLX mode only)
Keystroke: SHIFT then PAGE UP or ALT+C
- Close parenthesis (or RPN stack roll down)
Keystroke: PAGE DOWN or ) or ]
- M+
Add x to MEM memory
Keystroke: SHIFT then PAGE DOWN or ALT+NUM PLUS or ALT+"+" (plus)
- X<>Y
Exchange X and Y stack values
Keystroke: ALT+Y
- M-
Subtract x from MEM memory
Keystroke: ALT+NUM MINUS or ALT+"-" (minus)
- Numeric digit
Keystroke: 7 or NUM 7
- DOY <date>
Day of year (Jan 1st is 1)
Keystroke: SHIFT then 7 or SHIFT then NUM 7
- Numeric digit 8
Keystroke: 8 or NUM 8
- DOW <date>
Day of week (Monday is 1)
Keystroke: SHIFT then 8 or SHIFT then NUM 8
- Numeric digit 9
Keystroke: 9 or NUM 9
- WKNO <date>
Week number
Keystroke: SHIFT then 9 or SHIFT then NUM 9
- Backspace
Keystroke: BACKSPACE
- CLRMEM
Clear memory options
Keystroke: ALT+ESC
- All Clear
Keystroke: ESC or DELETE
- Numeric digit 4
Keystroke: 4 or NUM 4
- <f-date> 30A/360 <t-date>
Difference of dates using 30A/360 rule
Keystroke: SHIFT then 4 or SHIFT then NUM 4
- Numeric digit 5
Keystroke: 5 or NUM 5
- <f-date> 30E/360 <t-date>
Difference of dates using 30E/360 rule
Keystroke: SHIFT then 5 or SHIFT then NUM 5
- Numeric digit 6
Keystroke: 6 or NUM 6
- TODAY
Today's date & time
Keystroke: SHIFT then 6 or SHIFT then NUM 6
- Multiply
Keystroke: NUM MULTIPLY or "*" (multiply)
- <a + bi> : real
Real part of complex value
Keystroke: ALT+NUM MULTIPLY
- Divide
Keystroke: NUM DIVIDE or "/" (divide)
- <a + bi> : imag
Imaginary part of complex value
Keystroke: ALT+NUM DIVIDE
- Numeric digit 1
Keystroke: 1 or NUM 1
- <x> MOD <y>
Modulo of 2 arguments
Keystroke: SHIFT then 1 or SHIFT then NUM 1 or M
- Numeric digit 2
Keystroke: 2 or NUM 2
- <x> LCM <y>
Least common multiple of 2 arguments
Keystroke: SHIFT then 2 or SHIFT then NUM 2
- Numeric digit 3
Keystroke: 3 or NUM 3
- <x> GCD <y>
Greatest common denominator of 2 arguments
Keystroke: SHIFT then 3 or SHIFT then NUM 3
- Add
Keystroke: NUM PLUS or "+" (plus)
- <x> : iPart
Integer part of number
Keystroke: I or ALT+G
- Subtract
Keystroke: NUM MINUS or "-" (minus)
- <x> : fPart
Fraction part of number
Keystroke: F or ALT+J
- Numeric digit 0
Keystroke: 0 or NUM 0
- Rnd
Rounds value to display precision
Keystroke: SHIFT then 0 or SHIFT then NUM 0
- Decimal point
Keystroke: "." (period) or NUM DECIMAL
- DRGC
Convert input to the units of the calculator's angle mode
Keystroke: SHIFT then "." (period) or SHIFT then NUM DECIMAL
- Toggle sign or input (-) in MAL mode
Keystroke: SPACE
- Ans
Last answer (or LastX in RPN)
Keystroke: SHIFT then SPACE or ALT+X
- Input exponent value (also PI)
Keystroke: E or P
- NUM
Additional number theory functions
Keystroke: SHIFT then E or SHIFT then P or ALT+K
- Enter or equals
Keystroke: ENTER or "=" (equals)
- <x>%
Percentage value calculation
Keystroke: SHIFT then ENTER or %
Financial Keypad
If the financial keypad is in use, the following inputs take precedence.
- n# {i%, PV, PMT, FV}
Number of payments register
Keystroke: N
- 12×
Enter 12*x to the number of payments register
Keystroke: SHIFT then N
- i# {n, PV, PMT, FV}
Interest rate register
Keystroke: I
- 12÷
Input x/12 to the interest rate register
Keystroke: SHIFT then I
- PV# {n, i%, PMT, FV}
Present value register
Keystroke: V
- EAR <m-rate%>
Effective annual rate
Keystroke: SHIFT then V
- PMT# {n, i%, PV, FV}
Payment amount register
Keystroke: M
- EMR <y-rate%>
Effective monthly rate
Keystroke: SHIFT then M
- FV# {n, i%, PV, PMT}
Future value register
Keystroke: F
- INT {n, i%, PV}
Calculate simple interest
Keystroke: SHIFT then F
- NPV
Net present value & related functions menu
Keystroke: END
- BEG/END
Toggle compound interest mode
Keystroke: SHIFT then END or B
- IRR {cash-flow}
Internal rate of return
Keystroke: W
- SL <period> {n, PV, FV}
Straight-line depreciation
Keystroke: SHIFT then W
- MIRR <risk%> {i%, cash-flow}
Modified internal rate of return
Keystroke: U
- SOYD <period> {n, PV, FV}
Sum of years digit depreciation
Keystroke: SHIFT then U
- <f-date> PRICE <t-date> {n, i%, PMT}
Calculate bond price as percentage of par
Keystroke: P
- DB <period> {n, PV, FV}
Declining balance depreciation
Keystroke: SHIFT then P
- <f-date> YTM <t-date> {n, PV, PMT}
Calculate bond yield to maturity
Keystroke: Y
- AMORT <period> {i%, PV, FV}
Amortize payments calculation
Keystroke: SHIFT then Y
- CF0
Input initial cash-flow value
Keystroke: ALT+0 or ALT+NUM 0
- ROI {i%, cash-flow}
Return on investment
Keystroke: ALT+N
- CFj
Input consecutive cash-flow values
Keystroke: J
- Nj <N>
Add N repetitions of last cash-flow input
Keystroke: SHIFT then J
Base-N Mode
In the base-N mode, the following inputs take precedence.
- KB
Show Kilobytes & multiples of 1024
Keystroke: LEFT ARROW (or RIGHT ARROW)
- DEC
Set decimal radix
Keystroke: F7
- HEX
Set hex radix
Keystroke: F8
- BIN
Use binary radix
Keystroke: F9
- OCT
Use octal radix
Keystroke: F10
- <x> : SL
Integer shift left
Keystroke: < or ALT+LEFT ARROW
- <x> : SR
Integer shift right
Keystroke: > or ALT+RIGHT ARROW
- LOGIC
Base-N logic function menu
Keystroke: G
- Open parenthesis (or RPN stack roll up)
Keystroke: PAGE UP or ( or [
- Memory register A and base-N digit
Keystroke: A
- <x> REM <y>
Integer remainder
Keystroke: % or M or SHIFT then A
- Memory register B and base-N digit
Keystroke: B
- <x> AND <y>
Integer bitwise AND operator
Keystroke: & or ALT+A or SHIFT then B
- Memory register C and base-N digit
Keystroke: C
- <x> OR <y>
Integer bitwise OR operator
Keystroke: vert-bar or O or SHIFT then C
- Memory register D and base-N digit
Keystroke: D
- NOT <x>
Integer bitwise NOT operator
Keystroke: "!" (exclam) or "~" (tilda) or N or SHIFT then D
- Memory register E and base-N digit
Keystroke: E
- <x> XOR <y>
Integer bitwise XOR operator
Keystroke: X or SHIFT then E
- Memory register F and base-N digit
Keystroke: F
- <x> XNOR <y>
Integer bitwise XNOR operator
Keystroke: R or SHIFT then F
See also: Calculator Input Style


